Maximizing Lead-Based Battery Life: Essential Maintenance for Floor Cleaning Equipment
Imagine the frustration when your floor cleaning equipment stops mid-task—battery drained, productivity halted. Battery maintenance is crucial to ensure that this scenario is rare. Without it, your equipment's performance decreases, and your batteries' life span shortens dramatically. This article sheds light on the often overlooked yet critical practice of battery maintenance for floor cleaning machines.

From recognizing the diversity of battery types to emphasizing the importance of proper charging techniques and regular upkeep, we delve into strategies that can extend battery life and optimize equipment performance. With a comprehensive guide encompassing daily care routines, periodic check-ups, and storage tips, we provide insight into maintaining the heartbeat of your cleaning arsenal: the battery.
First and Foremost, Safety
Regardless of the type of battery used, there are some universal safety tips you should always follow:
- Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) - When working with batteries of any type, wear safety glasses and gloves to protect against potential hazards. If carrying batteries, protective footwear is recommended.
- Remove watches and jewelry - It is best to remove any conductive materials when working around batteries. In the event of a short circuit, metal objects like rings can heat rapidly, causing burns and electric shock.
- Use tools with insulated handles - If possible, using tools with insulated handles can reduce your chance of electric shock.
- No smoking, sparks,or open flames - Lead-acid batteries emit flammable hydrogen gas during charging. This includes sealed batteries, which generally hold most of the gas inside but could still pose a hazard if the seal is damaged.
- Maintain good ventilation - When working on or charging batteries, good ventilation reduces the risk of flammable gas and inhalation hazard.
- Never open sealed battery vents - Sealed batteries need to remain closed to function correctly. Removing the factory seal will damage the battery and void the warranty. If the seal appears damaged, discontinue use and call for service.
Types of Batteries (Flooded, AGM, and TPPL)
Flooded Lead-Acid Batteries - Sometimes called Wet Cell Batteries, are the lowest up-front cost batteries for cleaning equipment. These batteries require periodic inspection and maintenance to keep them operating. For this reason, its important to consider your maintenance costs when selecting the batteries for your cleaning equipment. Depending on your situation, sealed batteries may prove to be a lower-cost option when you include the required maintenance in the total cost of the equipment. There are complete instructions for maintaining flooded batteries further on in this article.
Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) Batteries - AGM (Absorbed Glass Mat) batteries use a glass mat separator to wick and suspend electrolyte, preventing spills even if the battery is damaged or tipped. The electrolyte is efficiently transferred from the mat to the battery plates, ensuring optimal performance and full capacity delivery. These batteries are maintenance-free, offer high discharge and recharge rates, and are resistant to vibration and impact. Their design enhances safety, durability, and lifespan compared to traditional flooded batteries.
Thin Plate Pure Lead (TPPL) Batteries - TPPL Batteries are a type of advanced sealed lead-acid battery that uses very thin plates made of pure lead. These thin plates increase the surface area, allowing for higher energy density and faster charge and discharge rates. TPPL batteries offer improved performance, longer lifespan, and greater efficiency compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. They are also more resistant to high temperatures and provide reliable power in demanding applications.
Both AGM and TPPL batteries are commonly referred to as "maintenance free" because the are sealed and unlike flooded batteries, don't need to have distilled water added periodically.

Proper Charging Techniques
To extend the service life of your floor cleaning equipment, proper charging techniques are imperative. Ensuring that the battery is fully charged after every use will maximize its longevity and operational efficiency. It is not advisable to leave a battery partially charged, as doing so can significantly reduce its life. Before operating the equipment, check the battery connections for tightness to ensure safety and prevent malfunctions.
Opportunity Charging vs. Full Charging
Opportunity Charging is the practice of charging batteries whenever time allows. For example, during a lunch break. While opportunity charging can provide some extra run time throughout the day, there are a few things to keep in mind:
- Opportunity charging doesn't replace full charge cycles - Battery chargers use a sophisticated program to make sure your batteries are optimally charged. If you only opportunity charge your batteries, the batteries never receive the full benefits of the charging algorithm and will eventually fail to perform.
- Opportunity charging is not recommended for flooded lead-acid batteries - Opportunity charging is not recommended for flooded lead-acid batteries because it can cause electrolyte stratification, sulfation, increased water consumption, and excessive heat generation, all of which reduce battery lifespan. These batteries perform best with full charge and discharge cycles and regular maintenance.
- Opportunity charging is ok for AGM batteries - Opportunity charging AGM batteries is allowed, with a few limitations. Opportunity charging AGM batteries is only recommended if the battery pack is over 50% charged. Also, the battery pack should go through a full charge cycle every day to minimize the impact of opportunity charging.
- Opportunity charging is allowed with TPPL batteries. - TPPL batteries tolerate opportunity charging well. Be sure that the batteries receive a full charge cycle at least once every seven days to minimize the impact of opportunity charging.
How to Complete a Full Charge Cycle
Important! The plates inside flooded batteries must be covered before charging. If the electrolyte level is below the level of the plates, add distilled water until the plates are covered. Do not fill the battery completely. The fluid level in the battery will rise during charging. If too full, it will overflow the battery. See the section below about maintaining electrolyte levels for flooded batteries for after-charging maintenance.
Batteries should be charged at the end of each shift. Fully charging batteries is a simple as plugging in the charger and allowing the charger to run until it's finished. The most common mistake is unplugging the charger before the cycle is completed. Depending on the size of the battery and how depleted it was, it can take 10 to 12 hours to fully charge the pack.
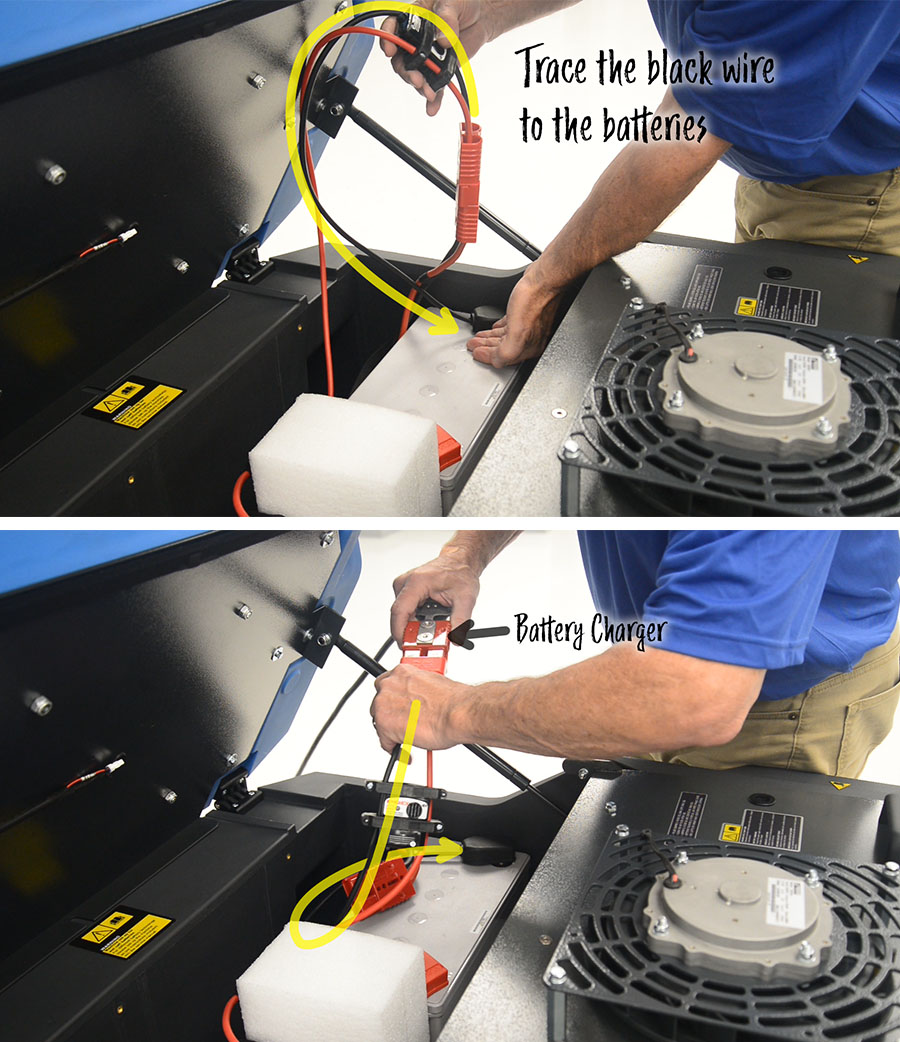
Connecting the Battery Charger
In some cases, users need to disconnect the battery pack from the machine to plug in the charger. When plugging in the charger, be sure to connect the charger to the battery pack. The charger plug can fit into both the machine side and the battery pack side of the connection. Connecting the charger to the machine will not charge the batteries.
To identify the correct connection for the battery charger, trace the black cable from the connector to the battery. See the example below.
Battery Charging Algorithms
IMPORTANT! If the charging algorithm is not correct, the battery pack will fail prematurely!
Battery charger manufacturers and battery manufacturers work hand-in-hand to make sure that each battery can be charged optimally. This often means that a battery charger will have several built-in algorithms to charge various types of batteries. If you change the brand of battery in a machine, you might need to change the charger's algorithm to ensure proper charging. The same is true if you change from flooded to sealed, or vice versa. Consult the charger's operation manual, or contact Hillyard Technical Service, for more information.
Battery Maintenance
Regular battery maintenance is essential for the efficiency and longevity of your floor cleaning equipment. Adhering to the manufacturer’s guidelines is foundational for preserving the battery life—this typically involves daily charging and cleaning.
Maintenance Tasks
- Clean battery terminals and connections - The health of battery terminals and connections is vital for the overall functionality of your equipment. Preventing overheating and sustaining electrical conductivity starts with routine assessments and maintenance of these points. Clean the terminals using a brush and a solution of one cup of baking soda per gallon of water. Do not allow the cleaning solution to get inside the battery.
- Check electrical connections to ensure they are properly tightened - Make sure that cable connections are tight. Loose connections can cause arcing, causing melting or possibly fire. Also, overtightening the electrical connection can break terminals resulting in loose connections. Consult your battery manufacturer's guidelines for the correct torque values.
- Inspect wire insulation for cracks - At least once a month, inspect battery cables for any signs of wear, such as insulation cracks. Immediately replace any wires with damaged insulation.
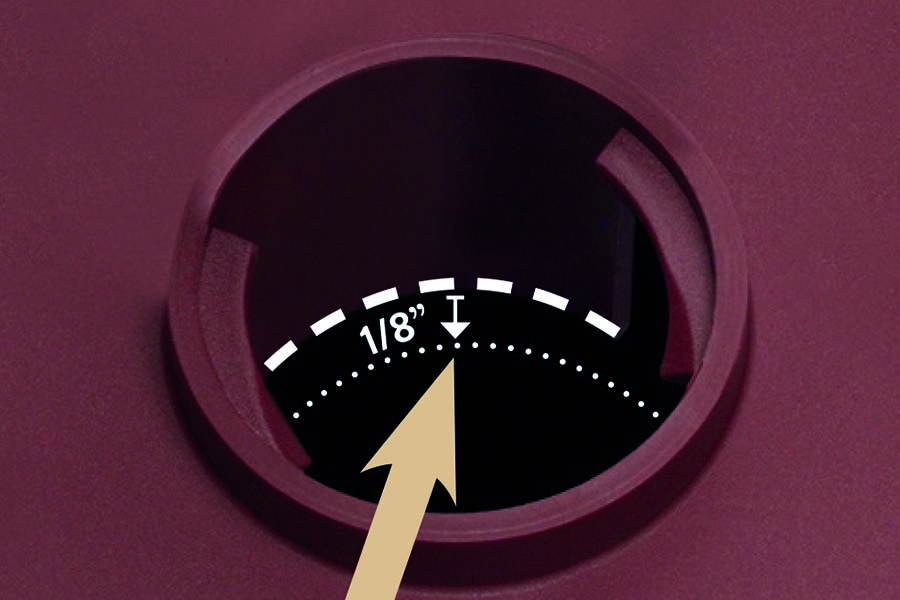
- Check water levels and refill with distilled water (Flooded Batteries Only) - For optimal battery performance of wet cell batteries, regular monitoring and replenishing of water levels using distilled water is a must. To prevent overfilling, it is best practice to add water only after the battery has gone through a complete charge cycle. Overfilling can cause the water to spill over during the next charging cycle, potentially resulting in irreversible damage to the battery. Neglecting the regular check and refilling can diminish the battery’s life by up to 50%. Add distilled water to charged batteries to a level of 1/8-inch below the vent well. See the image below.

Long-Term Storage of Equipment With Batteries
Storing floor cleaning equipment for an extended period might be necessary during off-seasons or when the equipment is not in regular use, such as in schools or offices during long holidays. Proper storage helps prevent wear and tear from environmental factors like dust, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, ensuring the equipment remains in good working condition.
Preparing Equipment for Extended Storage
When storing cleaning equipment, it is crucial to ensure that each item is thoroughly cleaned and dried beforehand. This prevents the buildup of mold, mildew, and unpleasant odors, which can occur if moisture is trapped on the equipment. Clean, dry equipment is also less likely to suffer from rust and corrosion, extending its lifespan and maintaining its effectiveness. Proper storage in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures, further protects the equipment.
Proper Storage of Batteries to Prevent Deterioration
When batteries are stored, they gradually lose their charge over time due to a phenomenon known as self-discharge. This process occurs because the chemical reactions within the battery continue at a slow rate, even when the battery is not in use. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and the type of battery can influence the rate of self-discharge, with higher temperatures accelerating the process. As a result, batteries can become depleted if left unused for extended periods, potentially affecting their performance and lifespan.
If possible, plug in the battery charger when putting a machine into storage. Chargers sold with Hillyard equipment continue to trickle charge the battery, keeping the pack voltage at the correct level. For flooded batteries, check the electrolyte level every six weeks while in storage.
If it's not possible to keep the charger plugged in, plan on charging the battery pack periodically to keep it in good condition.
- Flooded Batteries: Check the electrolyte level and charge the batteries every four to six weeks.
- AGM Batteries: Charge the batteries every two to three months.
- TPPL Batteries: Charge the batteries every two years.
Battery Warranty
The battery pack warranty will varies based on the type of battery. Based on Hillyard's equipment warranty, here's what you can expect:
Flooded Lead-Acid Batteries - Trojan Wet Batteries are covered by a 12-month pro-rated warranty.
Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) Batteries - Trojan AES Batteries are covered by a 3-year full replacement warranty.
Thin Plate Pure Lead (TPPL) Batteries - Enersys Nexsys TPPL Batteries are covered by a 3-year full replacement warranty and require the use of a Protection From Over-Discharge (POD) device.
For more details about Hillyard's Trident Equipment Warranty, click here to read the full policy
.
Hillyard Can Help You With Battery Questions
Proper battery maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your floor cleaning equipment. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can avoid unexpected downtimes and extend the life of your batteries. Hillyard has experts throughout the United States ready to assist with all your cleaning equipment and product needs. For personalized assistance, fill out the "I'm Interested" form to contact Hillyard and get tailored support from our knowledgeable team. Trust Hillyard to keep your cleaning operations running smoothly and efficiently.